Dental trauma is a major public health concern.
The impact of dental trauma is not only physical. It has psycho-social and economic consequences. In preschool children, oral trauma makes up 17% of all bodily injuries and its prevalence is up to 30% of permanent dentition world-wide.
In this issue, we will discuss dental trauma and the role of dentists in its management. Also, we will share specific home remedies in managing a dental crisis.
What is dental trauma?
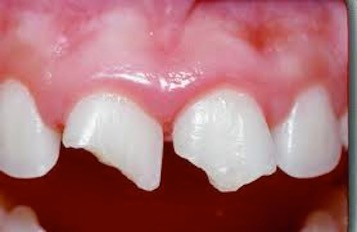
Dental trauma is injury to the mouth, teeth, lips, gums, tongue and jawbones. Soft tissue injuries to the mouth along with dental trauma are typically very painful and should receive prompt treatment. The most common dental trauma is a fractured front tooth or a tooth that was knocked out.
Clenching or teeth grinding is a form of dental trauma. Most people grind and clench their teeth from time to time. This type of dental trauma is called Bruxism. It can be destructive especially if it is done in excess. Bruxism causes your teeth to wear down and lose its enamel, sometimes causing damage to the underlying pulp.
Also, grinding may cause pain and soreness to your muscles used to chew. Further, clenching can cause severe pain in your teeth resulting in swelling and shaky teeth.
Teeth grinding and clenching are usually caused by stress or anxiety. In many cases, patients are unconscious of this habit because it is often a reflex action; sometimes even occurring while sleeping. Other reasons for grinding or clenching are crooked teeth, periodontal disease and sleep apnea.
How do you know you grind your teeth?
Many persons suffer a dull headache or soreness in their jaw when they awake. This is a common symptom of bruxism. Also, many people learn that they grind their teeth by their loved one who hears the grinding while asleep.
If there is concern, speak to a dentist. An examination will determine signs of bruxism, such as jaw tenderness and excessive wear on your teeth. In some cases; chronic teeth grinding can result in the fracturing, loosening or loss of teeth.
Broken or fractured teeth is the most common dental trauma. Serious fractures result in teeth becoming sensitive to touch, heat or cold. If the fracture causes an exposure of the inner most sensitive parts of the teeth such as the dentin or nerve pulp, then this can increase the risk of further complications. Some teeth are fractured or broken due to a large cavity that undermines the tooth leaving a shell. Eventually, the shell of the tooth collapses perhaps during normal chewing or biting into something hard.
Tooth Knocked out:
A more severe trauma may displace the tooth causing it to sink deeper into the socket or hang loosely out of it. If the blow is very severe, it may knock the tooth out completely or fracture the supporting bone. Common causes of knocked out teeth are sporting injuries, violence or an accident.
How to manage severe dental trauma?
If your tooth has been knocked out, loosened or fractured, visit the dentist as soon as possible. Seeing a dentist within 30 minutes can make the difference between saving or losing a tooth.
If your tooth has been knocked out, do the following:
- Find the tooth if you can and re-plant it immediately. If a baby tooth has been knocked out, it should not be replanted. Try to replace the tooth in the socket and keep it down by biting on a gauze. This will protect the periodontal ligament fibers surrounding the tooth.
- Always handle the tooth by the crown (biting surface). Do not touch the root; that is the part of the tooth below the gum. Touching the root can damage cells necessary for bone re-attachment. If there is any dirt on the tooth, do not try to scrape the tooth to remove it. Rinse gently with water.
- Apply a cold compress to your cheek to relieve any pain or swelling (within 30 minutes)
- If the tooth cannot be replaced in the socket bring the tooth to a dentist, without allowing it to dry out. Keep it moist by putting it in a small amount of cold milk or even in your own saliva.
Most dental traumas are preventable and controllable. If someone suffers from a form of dental trauma, see a dentist as soon as possible. If the trauma is caused by violence, consult your local authorities or police. Protect your teeth and gums by good hygiene practices. For sporting activities, use protective mouth guards. Good decisions save you money and engender good health and wellness.
Dr. Kendal V. O. Major is Founder and CEO of Center for Specialized Dentistry which is a comprehensive family dental practice operating in Nassau and Freeport. He is the first Bahamian Specialist in gum diseases and dental implants since 1989. He also is a certified Fast braces provider. His practice is located at 89 Collins Avenue, Nassau at (242)325-5165 or [email protected].


Most common dental trauma-front teeth of young children